... newer stories
Mittwoch, 24. Oktober 2007
Third class!!
Blanca.Delcastillo.Uni-Linz, 17:10h
In the third class we studied some points of the book as:
-Data compression :we saw an exampla of these kind of product which is the MP3.
-Construction and operation of the wise computer system:
-Hardware which have:-Central security.
-Peripheral.
-The enterprise system.
I am going to speak about the peripheral part of the hardware:
The pheripherie an computers serves three main purposes:
-The communication with the users.
-Maintenance of the data on the time away, and the date.
-Forums with other computer systems.
I am going to focus on the usb speak since I believe that the períferica memory of the computer is the fastest growing uses most people.
USB drive:
A flash memory card that plugs into the computer's USB port. Small enough to hook onto a keychain, it emulates a small disk drive and allows data to be easily transferred from one machine to another. Software drivers are not required for the latest operating systems, but are available on the Web for legacy systems such as Windows 98, Windows NT and Mac OS 8.
Transfer Speed
USB drive vendors claim to use the same data transfer ratings as CD-ROMs, where each "x" equals 150KB. However, their math is often imprecise. For example, a 90x drive may be rated at 14 MBps, but a simple multiplication yields a different number: 90 x 150 = 13.5MB).
Known By Many Names
Also known as a "flash drive," "pen drive," "keychain drive," "key drive," "USB key," "USB stick" and "memory key," numerous brand names have also been coined such as Lexar's JumpDrive and Trek 2000 International's ThumbDrive. Some products include synchronization software that keeps files updated between computers.


A Rotating Drive
The term may also refer to an external hard disk, CD or DVD drive that plugs into the computer's USB port. Whether portable or stationary, it is a regular disk drive and not a flash memory drive.
USB flash drive .
USB flash drives are NAND-type flash memory data storage devices integrated with a USB (universal serial bus) interface. They are typically small, lightweight, removable and rewritable. As of April 2007, memory capacities for USB Flash Drives currently are sold from 32 megabytes up to 64 gigabytes [1]. Capacity is limited only by current flash memory densities, although cost per megabyte may increase rapidly at higher capacities due to the expensive components. (USB Memory card readers are also available, whereby rather than being built-in, the memory is a removable Flash memory card housed in what is otherwise a regular USB flash drive, as described below.)
USB flash drives offer potential advantages over other portable storage devices, particularly the floppy disk. They are more compact, generally faster, hold more data, and are more reliable (due to both their lack of moving parts, and their more durable design) than floppy disks. These types of drives use the USB mass storage standard, supported natively by modern operating systems such as Linux, Mac OS X, Unix, and Windows.
A flash drive consists of a small printed circuit board encased in a plastic or metal casing, making the drive sturdy enough to be carried about in a pocket, as a key fob, or on a lanyard. Only the USB connector protrudes from this protection, and is usually covered by a removable cap. Most flash drives use a standard type-A USB connection allowing them to be connected directly to a port on a personal computer.
To access the data stored in a flash drive, the drive must be connected to a computer, either by plugging it into a USB host controller built into the computer, or into a USB hub. Flash drives are active only when plugged into a USB connection and draw all necessary power from the supply provided by that connection. However, some flash drives, especially high-speed drives utilizing the USB 2.0 standard, may require more power than the limited amount provided by a bus-powered USB hub, such as those built into some computer keyboards or monitors. These drives will not work unless plugged directly into a host controller (i.e., the ports found on the computer itself) or a self-powered hub.

First invention and sale
Several companies claim to be the first to have invented the USB Flash Drive in 1998 through 2000. Trek was the first company to sell a USB Flash Drive (ThumbDrive) in early 2000. However, their patent does not describe the USB Flash Drive; instead, it describes a very broad family of storage devices, of which the USB Flash Drive is one.
M-Systems (accquired by SanDisk in November 2006 ) has been working on developing the USB Flash Drive since 1998. The domain www.diskonkey.com was registered by them on October 12, 1999 and indicates that the USB Flash Drive was already in development. In 2000 Dan Harkabi joined the M-System team and led the development of DiskOnKey. The industrial design was done by Ziba and the product won the IDEA award in 2001. M-System's patent rigorously describes the USB Flash Drive and its implementation.
An IBM invention disclosure RPS8-1999-0201 (Sept. 99) by Shimon Shmueli et al is the earliest known document to accurately and completely describe the USB-FD, and only the USB-FD. M-Systems manufactured the DiskOnKey for IBM, who in late 2000 was the first to sell the product in North America. Shmueli later founded KeyNetica, the first company that patented and developed the concept that mobile and smart storage devices are all one needs for mobile computing. Current implementors of the concept are U3 (part of SanDisk that also owns the original KeyNetica patent) and Ceedo.
Trek Technology claims it was first to conceive and create the ThumbDrive . Henn stated:
"When we first introduced the ThumbDrive in early 2000, we believed that this little device was set to change the way consumers across the world would store and transport information and data," Trek 2000 Chief Executive Officer Henn Tan was quoted as saying. [Its potential] has made it essential for Trek to invest and protect its intellectual property ownership."
Trek holds patents for the ThumbDrive in Japan, Taiwan, South Korea, the United Kingdom, New Zealand and Singapore.
Nevertheless, the ownership of the patent for this device has been widely disputed. According to The Straits Times' report, other companies started marketing similar devices. M-Systems, which is listed on Nasdaq, called its gadgets DiskOnKey and Diskey. Electec is M-Systems' importer, and FE Global is its sole distributor in Singapore. Lexar can also lay claim to a pioneering USB flash drive product. In 2000 they introduced a Compact Flash (CF) card having an internal USB function. Lexar offered a companion card reader and USB cable that eliminated the need for a USB hub.
Trek sued the four companies for infringing its patent. They counterclaimed, asking that Trek's patent be revoked as it was invalid.
The Singapore Court of Appeals confirmed the validity of Trek Technology's patent for its ThumbDrive, calling it "novel and inventive" in the decision published in The Straits Times. The city-state's highest court also quashed the plea of four companies - Israeli firm M-Systems Flash Disk Pioneers, Electec, FE Global Electronics and Singapore-based Ritronics Components - and ordered them to stop selling similar devices. The decision is expected to have a ripple effect on other similar law suits which the Trek group has pending in Britain, Japan and Taiwan.
Netac Technology of Shenzhen, China also hold a 1999 Chinese and 2004 US patent on USB flash technology which they have licensed to major manufacturers.
Second generation
Modern flash drives have USB 2.0 connectivity. However, they do not currently use the full 480 Mbit/s the specification supports due to technical limitations inherent in NAND flash. The fastest drives currently available use a dual channel controller, although they still fall considerably short of the transfer rate possible from a current generation hard disk, or the maximum high speed USB 2.0 throughput.
Typical overall file transfer speeds are about 3 Mbytes/s. The highest current overall file transfer speeds are about 10-25 Mbytes/s. Older, "full speed" 12 Mbit/s devices are limited to a maximum of about 1 Mbytes/.
Components.
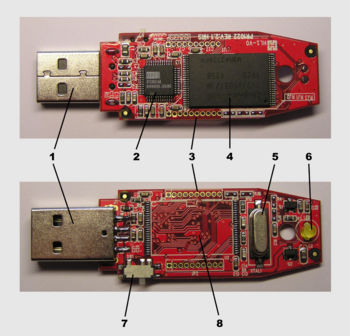
One end of the device is fitted with a single male type-A USB connector. Inside the plastic casing is a small printed circuit board. Mounted on this board is some simple power circuitry and a small number of surface-mounted integrated circuits (ICs). Typically, one of these ICs provides an interface to the USB port, another drives the onboard memory, and the other is the flash memory.
Essential components.
There are typically four parts to a flash drive:
Male type-A USB connector — provides an interface to the host computer.
USB mass storage controller — implements the USB host controller and provides a linear interface to block-oriented serial flash devices while hiding the complexities of block-orientation, block erasure, and wear levelling, or wear balancing. The controller contains a small RISC microprocessor and a small amount of on-chip ROM and RAM.
NAND flash memory chip — stores data. NAND flash is typically also used in digital cameras.
Crystal oscillator — produces the device's main 12 MHz clock signal and controls the device's data output through a phase-locked loop.
Additional components.
The typical device may also include:
Jumpers and test pins — for testing during the flash drive's manufacturing or loading code into the microprocessor.
LEDs — indicate data transfers or data reads and writes.
Write-protect switches — indicate whether the device should be in "write-protection" mode.
Unpopulated space — provides space to include a second memory chip. Having this second space allows the manufacturer to develop only one printed circuit board that can be used for more than one storage size device, to meet the needs of the market.
USB connector cover or cap — reduces the risk of damage due to static electricity, and improves overall device appearance. Some flash drives do not feature a cap, but instead have retractable USB connectors. Other flash drives have a "swivel" cap that is permanently connected to the drive itself and eliminates the chance of losing the cap.
Transport aid — In some cases, the cap or the main body contains a hole suitable for connection to a key chain or lanyard or to otherwise aid transport and storage of the USB flash device.
Size and style of packaging.
Some manufacturers differentiate their products by using elaborate housings, which are often bulky and make the drive difficult to connect to the USB port. Because the USB port connectors on a computer housing are often closely spaced, plugging a flash drive into a USB port may block an adjacent port. Such devices may only carry the USB logo if sold with a separate extension cable.
USB flash drives have been integrated into other things such as a watch or a pen.
Overweight or ill-fitting flash drive packaging can cause disconnection from the host computer. This can be overcome by using a short USB to USB (male to female) extension cable to relieve tension on the port. Such cables are USB-compatible, but do not conform to the USB standard
Common uses.
Personal data transport .
The most common use of flash drives is to transport and store personal files such as documents, pictures and video. Individuals also store medical alert information for use in emergencies and for disaster preparation.
Computer repair .
Flash drives enjoy notable success in the PC repair field as a means to transfer recovery and antivirus software to infected PCs, while allowing a portion of the host machine's data to be archived in case of emergency.
System administration.
Flash drives are particularly popular among system and network administrators, who load them with configuration information and software used for system maintenance, troubleshooting, and recovery.
Application carriers .
Flash drives are used to carry applications that run on the host computer without requiring installation. U3, backed by flash drive vendors, offers an API to flash drive-specific functions. A free and open-source software platform known as Portableapps has also been developed to allow U3-like functionality on non-U3 drives. airWRX is an application framework that runs from a flash drive and turns its PC host and other nearby PCs into a multi-screen, web-like work environment. The Mozilla Firefox browser has a configuration for flash drives, as does Opera.
Audio players .
Many companies make solid state digital audio players in a small form factor, essentially producing flash drives with sound output and a simple user interface. Probably the best-known of these has been Apple Computer's iPod shuffle, and the Creative Labs MuVo.
To boot operating systems .
In a way similar to that used in LiveCD, one can launch any operating system from a bootable flash drive, known as a LiveUSB.
In arcades .
In the arcade game In the Groove and more commonly In The Groove 2, flash drives are used to transfer high scores, screenshots, dance edits, and combos throughout sessions. While use of flash drives is common, the drive must be Linux compatible, causing problems for some players. Data used can then be uploaded to Groovestats.
Windows Vista ReadyBoost .
In Windows Vista, the ReadyBoost feature allows use of a flash drive to augment system memory.
Strengths and weaknesses.
Flash drives are nearly impervious to the scratches and dust that were problematic for previous forms of portable storage, such as compact discs and floppy disks, and their durable solid-state design means they often survive casual abuse. This makes them ideal for transporting personal data or work files from one location to another, such as from home to school or office or for carrying around personal data that the user typically wants to access in a variety of places. The near-ubiquity of USB support on modern computers means that such a drive will work in most places. A drawback to the small size is that they are easy to misplace, leave behind, or otherwise lose.
Flash drives are also a relatively dense form of storage, where even the cheapest will store dozens of floppy disks worth of data. Some can hold more data than a CD (700 MB). Top of the line flash drives can store more data than a double-sided dual-layer DVD - even 64 GB[1] and more.
Flash drives implement the USB mass storage device class, meaning that most modern operating systems can read and write to flash drives without any additional device drivers. The flash drives present a simple block-structured logical unit to the host operating system, hiding the individual complex implementation details of the various underlying flash memory devices. The operating system can use whatever type of filesystem or block addressing scheme it wants. Some computers have the ability to boot up from flash drives.
Like all flash memory devices, flash drives can sustain only a limited number of write and erase cycles before failure. Mid-range flash drives under normal conditions will support several hundred thousand cycles, although write operations will gradually slow as the device ages. This should be a consideration when using a flash drive to run application software or an operating system. To address this, as well as space limitations, some developers have produced special versions of operating systems (such as Linux) or commonplace applications (such as Mozilla Firefox) designed to run from flash drives. These are typically optimized for size and configured to place temporary or intermediate files in the computer's main RAM memory rather than store them temporarily on the flash drive.
Most USB flash drives do not include a write-protect mechanism. Such a switch on the housing of the drive itself would keep the host computer from writing or modifying data on the drive. Write-protection would make a device suitable for repairing virus-contaminated host computers without infecting the USB flash drive itself.
Flash drives are much more tolerant of abuse than mechanical drives, but can still be damaged or have data corrupted by severe physical impacts. Improperly wired USB ports can also destroy the circuitry of a flash drive, a danger in home-built desktop PCs.
Comparison to other portable memory forms.
Flash storage devices are often compared to other common, portable, swappable data storage devices, such as floppy disks, Zip disks, miniCD / miniDVD, CD-R/CD-RW and DVD-RW discs.
Floppy disks were the first popular method of file transport, but have been almost completely phased out due to their low capacity, low speed, and low durability. Virtually all new computers no longer include floppy drives, and do include USB ports, the Apple iMac being the first to ship this way. However, floppy disks are still in use because of their low cost; they are often the easiest or only way to share files with older systems; floppy drives can be added to new systems either internally or externally.
Attempts to extend the floppy standard (such as the Imation SuperDisk) were not successful because of a reputation for unreliability and the lack of a single standard for PC vendors to adopt. The Iomega Zip drive enjoyed some popularity, but never reached the point of ubiquity in computers. Also, the larger sizes of Zip—now up to 750 MB—cannot be read on older drives. Unless one were to carry an external drive, their usefulness as a means of moving data was rather limited. The cost per megabyte was fairly high, with individual disks often costing US$10 or more. Because moving parts are involved and the material used for creating the storage medium in Zip disks is similar to that used in floppy disks, Zip disks have a high risk of failure and data loss compared to flash drives. Larger removable storage media, like Iomega's Jaz drive, had even higher costs for both drives and media, and as such were not pervasively adopted as a floppy alternative.
CD-R and CD-RW are swappable storage media alternatives. Unlike Zip and floppy drives, DVD and CD recorders are now common in personal computer systems. CD-Rs can be written to only once. But CD-RWs are rated at up to 1,000 erase/write cycles, and modern NAND-based flash drives often last for 500,000 or more erase/write cycles. Optical storage devices also usually are slower than their flash-based counterparts. And, compact discs with a 12 cm diameter can be inconveniently large and, unlike flash drives, cannot fit into a pocket or hang from a key chain. There are smaller CD-R media such as business card CD-Rs, which have the same dimensions as a credit card, and (slightly less convenient but have more storage) 8 cm CD-Rs. But these are harder to obtain and generally more expensive than the standard 12 cm version. There also is no standard file system for rewritable optical media. Packet-writing utilities like DirectCD and InCD exist but produce discs that are not universally readable, despite their claiming to be based on the UDF standard. The upcoming Mount Rainier standard addresses this shortcoming in CD-RW media, but it still is not supported by most DVD and CD recorders or major operating systems. As a result, CDs/DVDs are a good way to record a great deal of information cheaply but not good for making ongoing small changes to a large collection of information; flash drives' ability to do this is their major advantage.
Security.
Some flash drives feature encryption of the data stored on them, generally using full disk encryption below the filesystem. This prevents an unauthorized person from accessing the data stored on it. The disadvantage is that the drive is accessible only in the minority of computers which have compatible encryption software, for which no portable standard is widely deployed.
Some encryption applications allow running without installation. The executable files can be stored on the USB drive, together with the encrypted file image. The encrypted partition can be accessed on any computer running Microsoft Windows. Other flash drives allow the user to configure secure and public partitions of different sizes. Executable files for Windows, Macintosh, and Linux may be on the drive, depending on manufacturer support. Some security software may require administrative rights on the host PC to access data.
Newer flash drives support biometric fingerprinting to confirm the user's identity. As of mid-2005, this was a relatively costly alternative to standard password protection offered on many new USB flash storage devices. Most fingerprint scanning drives rely upon the host operating system to validate the fingerprint via a software driver, restricting the drive to Microsoft Windows computers.
Some manufacturers deploy physical authentication tokens in the form of a flash drive. These are used to control access to a sensitive system by containing encryption keys or, more commonly, communicating with security software on the target machine. The system is designed so the target machine will not operate except when the flash drive device is plugged into it. Some of these "PC lock" devices also function as normal flash drives when plugged into other machines.
All such forms of data protection security involve an increased risk of loss of access to the data by the legitimate owner/user.
Flash drives present a significant security challenge for large organizations. Their small size and ease of use allows unsupervised visitors or unscrupulous employees to smuggle confidential data out with little chance of detection. Equally, corporate and public computers alike are vulnerable to attackers connecting a flash drive to a free USB port and using malicious software such as rootkits or packet sniffers. To prevent this, some organizations forbid the use of flash drives, and some computers are configured to disable the mounting of USB mass storage devices by ordinary users, a feature introduced in Windows XP Service Pack 2; others use third-party software to control USB usage. In a lower-tech security solution, some organizations disconnect USB ports inside the computer or fill the USB sockets with epoxy.
Naming.
Recently, "USB flash drive" or simply "UFD" has emerged as the de facto standard term for these devices. Many major manufacturers (SanDisk, Lexar, Kingston) and resellers use the term UFD to describe them. However, the myriad different brand names and terminology used, in the past and currently, makes UFDs more difficult for manufacturers to market and for consumers to research. Some commonly used names are actually trademarks of particular companies e.g. 'disgo'.
Future developments.
Semiconductor corporations have worked to reduce the cost of the components in a flash drive by integrating various flash drive functions in a single chip, thereby reducing the part-count and overall package cost.
Flash drive capacities on the market are continuously increasing. As of 2006, 64 MB and smaller capacity flash memory has been largely discontinued, and 128 MB capacity flash memory is being phased out. Kanguru has recently released a 64 GB flash memory drive that uses USB 2.0 and claims 10 years worth of information preservation.
Lexar is attempting to introduce a USB flash card, which would be a compact USB flash drive intended to replace various kinds of flash memory cards. Pretec introduced a similar card, which also plugs into every USB port, but is just one quarter the thickness of the Lexar model.
SanDisk has introduced a new technology to allow controlled storage and usage of copyrighted materials on flash drives, primarily for use by students. This technology is termed FlashCP.
In popular culture.
In 2004, the German punk band WIZO was the first musical group to release music in MP3 format on a USB drive, titled the WIZO Stick-EP.
In the films The Recruit and Collateral, thumb drives play an important role in the plot.
Some flash drives can retain their memory after being submerged in water , even through a machine wash. Leaving the flash drive out to dry completely before allowing current to run through it has been known to result in a working drive with no future problems.
Isolinear optical chips, fictional devices similar to USB drives in design and function, were featured regularly in Star Trek: The Next Generation over 10 years before their real world counterparts were invented.
On South Park a 1 GB flash drive was used to hold the Sword of a Thousand Truths which was previously removed from World of Warcraft in the episode Make Love, Not Warcraft.
On a recent episode of Prison Break a USB flash drive held an audio recording that was a key part of the plot of the show.
Music promoters left USB drives containing songs from the Nine Inch Nails album Year Zero in the bathrooms of several European concert venues prior to the album's 2007 release date.
-Data compression :we saw an exampla of these kind of product which is the MP3.
-Construction and operation of the wise computer system:
-Hardware which have:-Central security.
-Peripheral.
-The enterprise system.
I am going to speak about the peripheral part of the hardware:
The pheripherie an computers serves three main purposes:
-The communication with the users.
-Maintenance of the data on the time away, and the date.
-Forums with other computer systems.
I am going to focus on the usb speak since I believe that the períferica memory of the computer is the fastest growing uses most people.
USB drive:
A flash memory card that plugs into the computer's USB port. Small enough to hook onto a keychain, it emulates a small disk drive and allows data to be easily transferred from one machine to another. Software drivers are not required for the latest operating systems, but are available on the Web for legacy systems such as Windows 98, Windows NT and Mac OS 8.
Transfer Speed
USB drive vendors claim to use the same data transfer ratings as CD-ROMs, where each "x" equals 150KB. However, their math is often imprecise. For example, a 90x drive may be rated at 14 MBps, but a simple multiplication yields a different number: 90 x 150 = 13.5MB).
Known By Many Names
Also known as a "flash drive," "pen drive," "keychain drive," "key drive," "USB key," "USB stick" and "memory key," numerous brand names have also been coined such as Lexar's JumpDrive and Trek 2000 International's ThumbDrive. Some products include synchronization software that keeps files updated between computers.


A Rotating Drive
The term may also refer to an external hard disk, CD or DVD drive that plugs into the computer's USB port. Whether portable or stationary, it is a regular disk drive and not a flash memory drive.
USB flash drive .
USB flash drives are NAND-type flash memory data storage devices integrated with a USB (universal serial bus) interface. They are typically small, lightweight, removable and rewritable. As of April 2007, memory capacities for USB Flash Drives currently are sold from 32 megabytes up to 64 gigabytes [1]. Capacity is limited only by current flash memory densities, although cost per megabyte may increase rapidly at higher capacities due to the expensive components. (USB Memory card readers are also available, whereby rather than being built-in, the memory is a removable Flash memory card housed in what is otherwise a regular USB flash drive, as described below.)
USB flash drives offer potential advantages over other portable storage devices, particularly the floppy disk. They are more compact, generally faster, hold more data, and are more reliable (due to both their lack of moving parts, and their more durable design) than floppy disks. These types of drives use the USB mass storage standard, supported natively by modern operating systems such as Linux, Mac OS X, Unix, and Windows.
A flash drive consists of a small printed circuit board encased in a plastic or metal casing, making the drive sturdy enough to be carried about in a pocket, as a key fob, or on a lanyard. Only the USB connector protrudes from this protection, and is usually covered by a removable cap. Most flash drives use a standard type-A USB connection allowing them to be connected directly to a port on a personal computer.
To access the data stored in a flash drive, the drive must be connected to a computer, either by plugging it into a USB host controller built into the computer, or into a USB hub. Flash drives are active only when plugged into a USB connection and draw all necessary power from the supply provided by that connection. However, some flash drives, especially high-speed drives utilizing the USB 2.0 standard, may require more power than the limited amount provided by a bus-powered USB hub, such as those built into some computer keyboards or monitors. These drives will not work unless plugged directly into a host controller (i.e., the ports found on the computer itself) or a self-powered hub.

First invention and sale
Several companies claim to be the first to have invented the USB Flash Drive in 1998 through 2000. Trek was the first company to sell a USB Flash Drive (ThumbDrive) in early 2000. However, their patent does not describe the USB Flash Drive; instead, it describes a very broad family of storage devices, of which the USB Flash Drive is one.
M-Systems (accquired by SanDisk in November 2006 ) has been working on developing the USB Flash Drive since 1998. The domain www.diskonkey.com was registered by them on October 12, 1999 and indicates that the USB Flash Drive was already in development. In 2000 Dan Harkabi joined the M-System team and led the development of DiskOnKey. The industrial design was done by Ziba and the product won the IDEA award in 2001. M-System's patent rigorously describes the USB Flash Drive and its implementation.
An IBM invention disclosure RPS8-1999-0201 (Sept. 99) by Shimon Shmueli et al is the earliest known document to accurately and completely describe the USB-FD, and only the USB-FD. M-Systems manufactured the DiskOnKey for IBM, who in late 2000 was the first to sell the product in North America. Shmueli later founded KeyNetica, the first company that patented and developed the concept that mobile and smart storage devices are all one needs for mobile computing. Current implementors of the concept are U3 (part of SanDisk that also owns the original KeyNetica patent) and Ceedo.
Trek Technology claims it was first to conceive and create the ThumbDrive . Henn stated:
"When we first introduced the ThumbDrive in early 2000, we believed that this little device was set to change the way consumers across the world would store and transport information and data," Trek 2000 Chief Executive Officer Henn Tan was quoted as saying. [Its potential] has made it essential for Trek to invest and protect its intellectual property ownership."
Trek holds patents for the ThumbDrive in Japan, Taiwan, South Korea, the United Kingdom, New Zealand and Singapore.
Nevertheless, the ownership of the patent for this device has been widely disputed. According to The Straits Times' report, other companies started marketing similar devices. M-Systems, which is listed on Nasdaq, called its gadgets DiskOnKey and Diskey. Electec is M-Systems' importer, and FE Global is its sole distributor in Singapore. Lexar can also lay claim to a pioneering USB flash drive product. In 2000 they introduced a Compact Flash (CF) card having an internal USB function. Lexar offered a companion card reader and USB cable that eliminated the need for a USB hub.
Trek sued the four companies for infringing its patent. They counterclaimed, asking that Trek's patent be revoked as it was invalid.
The Singapore Court of Appeals confirmed the validity of Trek Technology's patent for its ThumbDrive, calling it "novel and inventive" in the decision published in The Straits Times. The city-state's highest court also quashed the plea of four companies - Israeli firm M-Systems Flash Disk Pioneers, Electec, FE Global Electronics and Singapore-based Ritronics Components - and ordered them to stop selling similar devices. The decision is expected to have a ripple effect on other similar law suits which the Trek group has pending in Britain, Japan and Taiwan.
Netac Technology of Shenzhen, China also hold a 1999 Chinese and 2004 US patent on USB flash technology which they have licensed to major manufacturers.
Second generation
Modern flash drives have USB 2.0 connectivity. However, they do not currently use the full 480 Mbit/s the specification supports due to technical limitations inherent in NAND flash. The fastest drives currently available use a dual channel controller, although they still fall considerably short of the transfer rate possible from a current generation hard disk, or the maximum high speed USB 2.0 throughput.
Typical overall file transfer speeds are about 3 Mbytes/s. The highest current overall file transfer speeds are about 10-25 Mbytes/s. Older, "full speed" 12 Mbit/s devices are limited to a maximum of about 1 Mbytes/.
Components.
One end of the device is fitted with a single male type-A USB connector. Inside the plastic casing is a small printed circuit board. Mounted on this board is some simple power circuitry and a small number of surface-mounted integrated circuits (ICs). Typically, one of these ICs provides an interface to the USB port, another drives the onboard memory, and the other is the flash memory.
Essential components.
There are typically four parts to a flash drive:
Male type-A USB connector — provides an interface to the host computer.
USB mass storage controller — implements the USB host controller and provides a linear interface to block-oriented serial flash devices while hiding the complexities of block-orientation, block erasure, and wear levelling, or wear balancing. The controller contains a small RISC microprocessor and a small amount of on-chip ROM and RAM.
NAND flash memory chip — stores data. NAND flash is typically also used in digital cameras.
Crystal oscillator — produces the device's main 12 MHz clock signal and controls the device's data output through a phase-locked loop.
Additional components.
The typical device may also include:
Jumpers and test pins — for testing during the flash drive's manufacturing or loading code into the microprocessor.
LEDs — indicate data transfers or data reads and writes.
Write-protect switches — indicate whether the device should be in "write-protection" mode.
Unpopulated space — provides space to include a second memory chip. Having this second space allows the manufacturer to develop only one printed circuit board that can be used for more than one storage size device, to meet the needs of the market.
USB connector cover or cap — reduces the risk of damage due to static electricity, and improves overall device appearance. Some flash drives do not feature a cap, but instead have retractable USB connectors. Other flash drives have a "swivel" cap that is permanently connected to the drive itself and eliminates the chance of losing the cap.
Transport aid — In some cases, the cap or the main body contains a hole suitable for connection to a key chain or lanyard or to otherwise aid transport and storage of the USB flash device.

Size and style of packaging.
Some manufacturers differentiate their products by using elaborate housings, which are often bulky and make the drive difficult to connect to the USB port. Because the USB port connectors on a computer housing are often closely spaced, plugging a flash drive into a USB port may block an adjacent port. Such devices may only carry the USB logo if sold with a separate extension cable.
USB flash drives have been integrated into other things such as a watch or a pen.
Overweight or ill-fitting flash drive packaging can cause disconnection from the host computer. This can be overcome by using a short USB to USB (male to female) extension cable to relieve tension on the port. Such cables are USB-compatible, but do not conform to the USB standard
Common uses.
Personal data transport .
The most common use of flash drives is to transport and store personal files such as documents, pictures and video. Individuals also store medical alert information for use in emergencies and for disaster preparation.
Computer repair .
Flash drives enjoy notable success in the PC repair field as a means to transfer recovery and antivirus software to infected PCs, while allowing a portion of the host machine's data to be archived in case of emergency.
System administration.
Flash drives are particularly popular among system and network administrators, who load them with configuration information and software used for system maintenance, troubleshooting, and recovery.
Application carriers .
Flash drives are used to carry applications that run on the host computer without requiring installation. U3, backed by flash drive vendors, offers an API to flash drive-specific functions. A free and open-source software platform known as Portableapps has also been developed to allow U3-like functionality on non-U3 drives. airWRX is an application framework that runs from a flash drive and turns its PC host and other nearby PCs into a multi-screen, web-like work environment. The Mozilla Firefox browser has a configuration for flash drives, as does Opera.
Audio players .
Many companies make solid state digital audio players in a small form factor, essentially producing flash drives with sound output and a simple user interface. Probably the best-known of these has been Apple Computer's iPod shuffle, and the Creative Labs MuVo.
To boot operating systems .
In a way similar to that used in LiveCD, one can launch any operating system from a bootable flash drive, known as a LiveUSB.
In arcades .
In the arcade game In the Groove and more commonly In The Groove 2, flash drives are used to transfer high scores, screenshots, dance edits, and combos throughout sessions. While use of flash drives is common, the drive must be Linux compatible, causing problems for some players. Data used can then be uploaded to Groovestats.
Windows Vista ReadyBoost .
In Windows Vista, the ReadyBoost feature allows use of a flash drive to augment system memory.
Strengths and weaknesses.
Flash drives are nearly impervious to the scratches and dust that were problematic for previous forms of portable storage, such as compact discs and floppy disks, and their durable solid-state design means they often survive casual abuse. This makes them ideal for transporting personal data or work files from one location to another, such as from home to school or office or for carrying around personal data that the user typically wants to access in a variety of places. The near-ubiquity of USB support on modern computers means that such a drive will work in most places. A drawback to the small size is that they are easy to misplace, leave behind, or otherwise lose.
Flash drives are also a relatively dense form of storage, where even the cheapest will store dozens of floppy disks worth of data. Some can hold more data than a CD (700 MB). Top of the line flash drives can store more data than a double-sided dual-layer DVD - even 64 GB[1] and more.
Flash drives implement the USB mass storage device class, meaning that most modern operating systems can read and write to flash drives without any additional device drivers. The flash drives present a simple block-structured logical unit to the host operating system, hiding the individual complex implementation details of the various underlying flash memory devices. The operating system can use whatever type of filesystem or block addressing scheme it wants. Some computers have the ability to boot up from flash drives.
Like all flash memory devices, flash drives can sustain only a limited number of write and erase cycles before failure. Mid-range flash drives under normal conditions will support several hundred thousand cycles, although write operations will gradually slow as the device ages. This should be a consideration when using a flash drive to run application software or an operating system. To address this, as well as space limitations, some developers have produced special versions of operating systems (such as Linux) or commonplace applications (such as Mozilla Firefox) designed to run from flash drives. These are typically optimized for size and configured to place temporary or intermediate files in the computer's main RAM memory rather than store them temporarily on the flash drive.
Most USB flash drives do not include a write-protect mechanism. Such a switch on the housing of the drive itself would keep the host computer from writing or modifying data on the drive. Write-protection would make a device suitable for repairing virus-contaminated host computers without infecting the USB flash drive itself.
Flash drives are much more tolerant of abuse than mechanical drives, but can still be damaged or have data corrupted by severe physical impacts. Improperly wired USB ports can also destroy the circuitry of a flash drive, a danger in home-built desktop PCs.
Comparison to other portable memory forms.
Flash storage devices are often compared to other common, portable, swappable data storage devices, such as floppy disks, Zip disks, miniCD / miniDVD, CD-R/CD-RW and DVD-RW discs.
Floppy disks were the first popular method of file transport, but have been almost completely phased out due to their low capacity, low speed, and low durability. Virtually all new computers no longer include floppy drives, and do include USB ports, the Apple iMac being the first to ship this way. However, floppy disks are still in use because of their low cost; they are often the easiest or only way to share files with older systems; floppy drives can be added to new systems either internally or externally.
Attempts to extend the floppy standard (such as the Imation SuperDisk) were not successful because of a reputation for unreliability and the lack of a single standard for PC vendors to adopt. The Iomega Zip drive enjoyed some popularity, but never reached the point of ubiquity in computers. Also, the larger sizes of Zip—now up to 750 MB—cannot be read on older drives. Unless one were to carry an external drive, their usefulness as a means of moving data was rather limited. The cost per megabyte was fairly high, with individual disks often costing US$10 or more. Because moving parts are involved and the material used for creating the storage medium in Zip disks is similar to that used in floppy disks, Zip disks have a high risk of failure and data loss compared to flash drives. Larger removable storage media, like Iomega's Jaz drive, had even higher costs for both drives and media, and as such were not pervasively adopted as a floppy alternative.
CD-R and CD-RW are swappable storage media alternatives. Unlike Zip and floppy drives, DVD and CD recorders are now common in personal computer systems. CD-Rs can be written to only once. But CD-RWs are rated at up to 1,000 erase/write cycles, and modern NAND-based flash drives often last for 500,000 or more erase/write cycles. Optical storage devices also usually are slower than their flash-based counterparts. And, compact discs with a 12 cm diameter can be inconveniently large and, unlike flash drives, cannot fit into a pocket or hang from a key chain. There are smaller CD-R media such as business card CD-Rs, which have the same dimensions as a credit card, and (slightly less convenient but have more storage) 8 cm CD-Rs. But these are harder to obtain and generally more expensive than the standard 12 cm version. There also is no standard file system for rewritable optical media. Packet-writing utilities like DirectCD and InCD exist but produce discs that are not universally readable, despite their claiming to be based on the UDF standard. The upcoming Mount Rainier standard addresses this shortcoming in CD-RW media, but it still is not supported by most DVD and CD recorders or major operating systems. As a result, CDs/DVDs are a good way to record a great deal of information cheaply but not good for making ongoing small changes to a large collection of information; flash drives' ability to do this is their major advantage.
Security.
Some flash drives feature encryption of the data stored on them, generally using full disk encryption below the filesystem. This prevents an unauthorized person from accessing the data stored on it. The disadvantage is that the drive is accessible only in the minority of computers which have compatible encryption software, for which no portable standard is widely deployed.
Some encryption applications allow running without installation. The executable files can be stored on the USB drive, together with the encrypted file image. The encrypted partition can be accessed on any computer running Microsoft Windows. Other flash drives allow the user to configure secure and public partitions of different sizes. Executable files for Windows, Macintosh, and Linux may be on the drive, depending on manufacturer support. Some security software may require administrative rights on the host PC to access data.
Newer flash drives support biometric fingerprinting to confirm the user's identity. As of mid-2005, this was a relatively costly alternative to standard password protection offered on many new USB flash storage devices. Most fingerprint scanning drives rely upon the host operating system to validate the fingerprint via a software driver, restricting the drive to Microsoft Windows computers.
Some manufacturers deploy physical authentication tokens in the form of a flash drive. These are used to control access to a sensitive system by containing encryption keys or, more commonly, communicating with security software on the target machine. The system is designed so the target machine will not operate except when the flash drive device is plugged into it. Some of these "PC lock" devices also function as normal flash drives when plugged into other machines.
All such forms of data protection security involve an increased risk of loss of access to the data by the legitimate owner/user.
Flash drives present a significant security challenge for large organizations. Their small size and ease of use allows unsupervised visitors or unscrupulous employees to smuggle confidential data out with little chance of detection. Equally, corporate and public computers alike are vulnerable to attackers connecting a flash drive to a free USB port and using malicious software such as rootkits or packet sniffers. To prevent this, some organizations forbid the use of flash drives, and some computers are configured to disable the mounting of USB mass storage devices by ordinary users, a feature introduced in Windows XP Service Pack 2; others use third-party software to control USB usage. In a lower-tech security solution, some organizations disconnect USB ports inside the computer or fill the USB sockets with epoxy.
Naming.
Recently, "USB flash drive" or simply "UFD" has emerged as the de facto standard term for these devices. Many major manufacturers (SanDisk, Lexar, Kingston) and resellers use the term UFD to describe them. However, the myriad different brand names and terminology used, in the past and currently, makes UFDs more difficult for manufacturers to market and for consumers to research. Some commonly used names are actually trademarks of particular companies e.g. 'disgo'.
Future developments.
Semiconductor corporations have worked to reduce the cost of the components in a flash drive by integrating various flash drive functions in a single chip, thereby reducing the part-count and overall package cost.
Flash drive capacities on the market are continuously increasing. As of 2006, 64 MB and smaller capacity flash memory has been largely discontinued, and 128 MB capacity flash memory is being phased out. Kanguru has recently released a 64 GB flash memory drive that uses USB 2.0 and claims 10 years worth of information preservation.
Lexar is attempting to introduce a USB flash card, which would be a compact USB flash drive intended to replace various kinds of flash memory cards. Pretec introduced a similar card, which also plugs into every USB port, but is just one quarter the thickness of the Lexar model.
SanDisk has introduced a new technology to allow controlled storage and usage of copyrighted materials on flash drives, primarily for use by students. This technology is termed FlashCP.
In popular culture.
In 2004, the German punk band WIZO was the first musical group to release music in MP3 format on a USB drive, titled the WIZO Stick-EP.
In the films The Recruit and Collateral, thumb drives play an important role in the plot.
Some flash drives can retain their memory after being submerged in water , even through a machine wash. Leaving the flash drive out to dry completely before allowing current to run through it has been known to result in a working drive with no future problems.
Isolinear optical chips, fictional devices similar to USB drives in design and function, were featured regularly in Star Trek: The Next Generation over 10 years before their real world counterparts were invented.
On South Park a 1 GB flash drive was used to hold the Sword of a Thousand Truths which was previously removed from World of Warcraft in the episode Make Love, Not Warcraft.
On a recent episode of Prison Break a USB flash drive held an audio recording that was a key part of the plot of the show.
Music promoters left USB drives containing songs from the Nine Inch Nails album Year Zero in the bathrooms of several European concert venues prior to the album's 2007 release date.
... link (0 comments) ... comment
Second class!!!
Blanca.Delcastillo.Uni-Linz, 16:03h
We stuided in the second class:
1.1.4.Software ergonomics
The software ergonomics deals with the adjustment of Benutzerschittstelle to the people and its peculiarities in receiving and processing information and knowledge.Software ergonomics is a science in which evidence from psychology, industrial science and the science together led, in order to systematically design goals for tasks appropriate and user-human-computer systems to work.
Three design fields are in the framework of software ergonomics important: the labor system, the dialog behavior and the input / output behavior of computer systems.They determine the user interface for the user than the visible part of an interactive system.
1.1.5 Interaction Techniques
Over time, a number of techniques have emerged Interaction.Their use is primarily dependent on the hardware, software and usage of the situation.
The interaction of the user with the computer is dialogue, there is a mutual exchange of information between the two plays.A specific change has been exacerbated by the personal computer and the capacity of the systems multitasking allowing the user can simultaneously carry a wide variety of actions.Regarding a dialogue with the old thread interplay of dialogue.
1.1.5.1. Command Language
A command language is a formal language for the formulation of orders to the computer. For each contract will require information such operation, in text form.Missing information will be supplemented by standard values, which are fixed or current condition to be removed.
-Major design issues for command languages are:
a)The application design vocabulary
b)The design of abbreviations based on uniform and simple rules
c)The single syntactic structure of commands
d)The comprehensive description of the linguistic expression of possibilities
-Advantages:
a)They require no special input devices, which are usually available keyboard
b)They allow the easy recording of past
c)The experienced user can very quickly and efficiently work
d)There are powerful commands feasible
-disadvantages
a)High learning, especially for novice and occasional users. It is a use without knowledge of the syntax is not possible.
b)The input is error-prone because commands and parameters need to be reminded
c)Because of the impact area commands of the entire state of the interactive system, it is difficult, the effects of a commando directly control
1.1.5.2. Menu
Through menus, the selection of actions defined in scope.The user chooses from a list of the desired command, which is executed by the computer.If parameters or settings are needed for entering a corresponding further dialogue open.Different types of menus are: permanent fully or partially visible menus and menus displayed on request.For the usability of the menus is their structuring important, it can be a menu item in turn is a sub-menu.This structure can be used in the width and depth.
-Advantages
a)Easy to learn, since commands recognized, and not have to be reminded.
b)Low error rate, since in principle for a command no errors are possible.
-Disadvantages
a)For experienced users is cumbersome to operate and lasts long
b)The menus are superimposed Anwedungsinformationen
1.1.5.4.Direct manipulation.
This dialog is based on the style exist an instrument show how z.b. The Maus.Der dialog is similar to natural negotiations, it is an object and then select the desired possible negotiations on this subject.
Advantages:
-Low-lernauf wand, as the use in many cases intuitively possible.
- Through the use of known metaphors is a faster erlernbarkeit by the tying of new and old know promoted.
-He is a fast efficient use of the systems is reached, which even for experts in the cases is sufficient.
-Promotion of exploratory learning, it is the users fear a possible use, which his competence-and kontroll awareness increased.
Disadvantages:
- Inexperienced users need only show the use of the instrument to learn.
- Inadequate analogien between the routine and know the realization comes to metaphor breaks.
- Through the use intuitive ability is the acquisition of specific knowledge, in many cases prevented.
Graphical interface benut.
Graphical interface benut Often in a breath with the direct manipulation Grande, but usually in a mixture of rankig interaktions techniques.
1.1.5.5.1. leitideen.
The leitideen for graphical benut zero over surfaces.
Users control .
visuella show and also kontroll possibility of automatic transactions, feeling of control.
Feedback.
Echo or any reaction to provide input,
- Pointer changes form
-Object-changing look.
-Menu entry is pale, if not selectable.
-Sattus-row shows progress by the bar or length files.
-Over-view window shows chrittan forts.
- Window event.
Directness.
Visualles equivalent of the data and functions to show.
Use of logic metephern
Examples: desk with benches, entr skorb, bin, mappen.
Advantages: user has information about sinn and function of the object.
Consistency.
Similar situations
Out-of selectable menu also show.
Data secure document print: always file from choice or always without.
Simplicity.
Short messages and commands.
Aesthetics.
A conflict vitlab.m, vs. functionality. Beauty.
Benutzeroberflächen graphical elements.
Fenster.
The screen can be divided into several excerpts, which refers to as a window warden .Fenster are rectangular and graphically by seuten pointers begrenzt .Fenster allow control of multiple, overlapping one another kepekchirmausschinitte, which work directly excerpts users can be assigned.
The following operations window systems should be made available:
- Create.
- Delete.
- Open: opens a window in a reduced representation, such as pictograms or bar graph.
- Close: 1 Fenstre reduced to a pictogram or Blaken.
- Move: Allowed moving (pulling) of a window on the screen without the size of the window to change.
- Resize: dirce a size variation of the window.
- Full Size: The maximum allowed immediately extend a window.
- Small Size: a window directly reduced to its minimum size.
- Scroll: lets the window vertically or horizontally happen ...
- Define: allows the definition of a window.
- Bring-to-front: takes the selected window in the foreground image (for overlapping windows).
- Sent-to-back: moves the selected window in the background (with overlapping windows).
- Menu bar: often at the top level windows
- Pull-down menu is visible, unless or until mouse is pressed for example On menu bar anchored. It opens to the bottom, when you move the mouse pointer over the menu title runs.
- Drop-down menu appears, without that mouse button, the cursor will only object moving.
- Context menus: A pop-up can only be in the places in an application to be opened where it makes sense. It can be special tools or a command selection, which in this section of the software can be used and can be anywhere on the screen.
Symbols (icons)
Graphic symbols, the use of computers, instruments, but also with graphical display. The SYmbole represent different objects, such as documents, windows, actions, ...
Icons are used for the representation of:
Components
Processes
Expiration end processes with the possibility of interference
Buttons
Command button to play an important role in the interaction between humans and computers. Command buttons are available as Cancel, OK or command button available.
Check boxes are a way to select any one or more options to realize.
Option buttons can always just one of several
Dialogboxen
TextBox: It serves to enter alphanumeric data on the keyboard or the clipboard to a program. Input fields can occur in several variants: Single line or multiline, scrollbars can optionally be displayed, the maximum length of text can be set.
Listbox is used to give the user the ability to give out a list oedr several items.
Leisten (Bars)
Toolbar is composed of one or several buttons, for example, performed to edit files such as Save, Open.
StatusBar is used to provide information about the status of an application.
Progressbar is used to inform the user about the progress of a process to inform.
Register consists of one or more flaps, which always can be selected.
Slider will find their application, where the user has a value of a fixed set of numerical values linearly arranged with constant Abstënden.
Ansichten
Baumansicht is used to collect data in a tree structure. Example of this is the file system. These nodes can be further nodes and leaves. Leaves are node, the node no further information.
Listenansicht is used by several elements. It is possible to select multiple columns and graphics for the elements firmly.
Dialogues
During the dialogue and interaction management, the intuitive operation of the user support:
Ideally, the user should be to him on the screen just as well-known symbols real objects can be manipulated.
Where object-action principle: Only select object, then the object for the kinds of actions an action.
Order input masks in traditional programs will be rigidly set, the program guides the user that he has less Freihieten.
1.1.4.Software ergonomics
The software ergonomics deals with the adjustment of Benutzerschittstelle to the people and its peculiarities in receiving and processing information and knowledge.Software ergonomics is a science in which evidence from psychology, industrial science and the science together led, in order to systematically design goals for tasks appropriate and user-human-computer systems to work.
Three design fields are in the framework of software ergonomics important: the labor system, the dialog behavior and the input / output behavior of computer systems.They determine the user interface for the user than the visible part of an interactive system.
1.1.5 Interaction Techniques
Over time, a number of techniques have emerged Interaction.Their use is primarily dependent on the hardware, software and usage of the situation.
The interaction of the user with the computer is dialogue, there is a mutual exchange of information between the two plays.A specific change has been exacerbated by the personal computer and the capacity of the systems multitasking allowing the user can simultaneously carry a wide variety of actions.Regarding a dialogue with the old thread interplay of dialogue.
1.1.5.1. Command Language
A command language is a formal language for the formulation of orders to the computer. For each contract will require information such operation, in text form.Missing information will be supplemented by standard values, which are fixed or current condition to be removed.
-Major design issues for command languages are:
a)The application design vocabulary
b)The design of abbreviations based on uniform and simple rules
c)The single syntactic structure of commands
d)The comprehensive description of the linguistic expression of possibilities
-Advantages:
a)They require no special input devices, which are usually available keyboard
b)They allow the easy recording of past
c)The experienced user can very quickly and efficiently work
d)There are powerful commands feasible
-disadvantages
a)High learning, especially for novice and occasional users. It is a use without knowledge of the syntax is not possible.
b)The input is error-prone because commands and parameters need to be reminded
c)Because of the impact area commands of the entire state of the interactive system, it is difficult, the effects of a commando directly control
1.1.5.2. Menu
Through menus, the selection of actions defined in scope.The user chooses from a list of the desired command, which is executed by the computer.If parameters or settings are needed for entering a corresponding further dialogue open.Different types of menus are: permanent fully or partially visible menus and menus displayed on request.For the usability of the menus is their structuring important, it can be a menu item in turn is a sub-menu.This structure can be used in the width and depth.
-Advantages
a)Easy to learn, since commands recognized, and not have to be reminded.
b)Low error rate, since in principle for a command no errors are possible.
-Disadvantages
a)For experienced users is cumbersome to operate and lasts long
b)The menus are superimposed Anwedungsinformationen
1.1.5.4.Direct manipulation.
This dialog is based on the style exist an instrument show how z.b. The Maus.Der dialog is similar to natural negotiations, it is an object and then select the desired possible negotiations on this subject.
Advantages:
-Low-lernauf wand, as the use in many cases intuitively possible.
- Through the use of known metaphors is a faster erlernbarkeit by the tying of new and old know promoted.
-He is a fast efficient use of the systems is reached, which even for experts in the cases is sufficient.
-Promotion of exploratory learning, it is the users fear a possible use, which his competence-and kontroll awareness increased.
Disadvantages:
- Inexperienced users need only show the use of the instrument to learn.
- Inadequate analogien between the routine and know the realization comes to metaphor breaks.
- Through the use intuitive ability is the acquisition of specific knowledge, in many cases prevented.
Graphical interface benut.
Graphical interface benut Often in a breath with the direct manipulation Grande, but usually in a mixture of rankig interaktions techniques.
1.1.5.5.1. leitideen.
The leitideen for graphical benut zero over surfaces.
Users control .
visuella show and also kontroll possibility of automatic transactions, feeling of control.
Feedback.
Echo or any reaction to provide input,
- Pointer changes form
-Object-changing look.
-Menu entry is pale, if not selectable.
-Sattus-row shows progress by the bar or length files.
-Over-view window shows chrittan forts.
- Window event.
Directness.
Visualles equivalent of the data and functions to show.
Use of logic metephern
Examples: desk with benches, entr skorb, bin, mappen.
Advantages: user has information about sinn and function of the object.
Consistency.
Similar situations
Out-of selectable menu also show.
Data secure document print: always file from choice or always without.
Simplicity.
Short messages and commands.
Aesthetics.
A conflict vitlab.m, vs. functionality. Beauty.
Benutzeroberflächen graphical elements.
Fenster.
The screen can be divided into several excerpts, which refers to as a window warden .Fenster are rectangular and graphically by seuten pointers begrenzt .Fenster allow control of multiple, overlapping one another kepekchirmausschinitte, which work directly excerpts users can be assigned.
The following operations window systems should be made available:
- Create.
- Delete.
- Open: opens a window in a reduced representation, such as pictograms or bar graph.
- Close: 1 Fenstre reduced to a pictogram or Blaken.
- Move: Allowed moving (pulling) of a window on the screen without the size of the window to change.
- Resize: dirce a size variation of the window.
- Full Size: The maximum allowed immediately extend a window.
- Small Size: a window directly reduced to its minimum size.
- Scroll: lets the window vertically or horizontally happen ...
- Define: allows the definition of a window.
- Bring-to-front: takes the selected window in the foreground image (for overlapping windows).
- Sent-to-back: moves the selected window in the background (with overlapping windows).
- Menu bar: often at the top level windows
- Pull-down menu is visible, unless or until mouse is pressed for example On menu bar anchored. It opens to the bottom, when you move the mouse pointer over the menu title runs.
- Drop-down menu appears, without that mouse button, the cursor will only object moving.
- Context menus: A pop-up can only be in the places in an application to be opened where it makes sense. It can be special tools or a command selection, which in this section of the software can be used and can be anywhere on the screen.
Symbols (icons)
Graphic symbols, the use of computers, instruments, but also with graphical display. The SYmbole represent different objects, such as documents, windows, actions, ...
Icons are used for the representation of:
Components
Processes
Expiration end processes with the possibility of interference
Buttons
Command button to play an important role in the interaction between humans and computers. Command buttons are available as Cancel, OK or command button available.
Check boxes are a way to select any one or more options to realize.
Option buttons can always just one of several
Dialogboxen
TextBox: It serves to enter alphanumeric data on the keyboard or the clipboard to a program. Input fields can occur in several variants: Single line or multiline, scrollbars can optionally be displayed, the maximum length of text can be set.
Listbox is used to give the user the ability to give out a list oedr several items.
Leisten (Bars)
Toolbar is composed of one or several buttons, for example, performed to edit files such as Save, Open.
StatusBar is used to provide information about the status of an application.
Progressbar is used to inform the user about the progress of a process to inform.
Register consists of one or more flaps, which always can be selected.
Slider will find their application, where the user has a value of a fixed set of numerical values linearly arranged with constant Abstënden.
Ansichten
Baumansicht is used to collect data in a tree structure. Example of this is the file system. These nodes can be further nodes and leaves. Leaves are node, the node no further information.
Listenansicht is used by several elements. It is possible to select multiple columns and graphics for the elements firmly.
Dialogues
During the dialogue and interaction management, the intuitive operation of the user support:
Ideally, the user should be to him on the screen just as well-known symbols real objects can be manipulated.
Where object-action principle: Only select object, then the object for the kinds of actions an action.
Order input masks in traditional programs will be rigidly set, the program guides the user that he has less Freihieten.
... link (0 comments) ... comment
... older stories
Online for 6474 days
Last update: 2008.01.28, 21:37
Last update: 2008.01.28, 21:37
status
You're not logged in ... login
menu
search
calendar
Oktober 2007 |
||||||
Mo |
Di |
Mi |
Do |
Fr |
Sa |
So |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
||
29 |
30 |
31 |
||||
recent updates
These is the end!!!!!(1st...
Well the semester is going to finished and with these...
Well the semester is going to finished and with these...
by Blanca.Delcastillo.Uni-Linz (2008.01.28, 21:37)
These is the end!!!!!(1st...
Well the semester is going to finished and with these...
Well the semester is going to finished and with these...
by Blanca.Delcastillo.Uni-Linz (2008.01.28, 21:36)
These is the end!!!!!(1st...
Well the semester is going to finished and with these...
Well the semester is going to finished and with these...
by Blanca.Delcastillo.Uni-Linz (2008.01.28, 21:33)
These is the end!!!!
Well the semester is going to finished and with these...
Well the semester is going to finished and with these...
by Blanca.Delcastillo.Uni-Linz (2008.01.28, 21:28)
These is the end!!!!
Well the semester is going to finished and with these...
Well the semester is going to finished and with these...
by Blanca.Delcastillo.Uni-Linz (2008.01.28, 21:26)